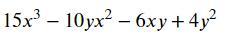Answer:
a)Ideal gas:
An ideal gas is defined as a gas that obeys gas laws at all conditions of pressure and temperature. Ideal gases have velocity and mass. They do not have volume. When compared to the total volume of the gas the volume occupied by the gas is negligible. It does not condense and does not have triple point.
A real gas is defined as a gas that does not obey gas laws at all standard pressure and temperature conditions. When the gas becomes massive and voluminous it deviates from its ideal behaviour. Real gases have velocity, volume and mass. When they are cooled to their boiling point, they liquefy. When compared to the total volume of the gas the volume occupied by the gas is not negligible.
To make you understand how ideal gas and real gas are different from each other, here are some of the major differences between ideal gas and real gas:
b) The term "Electric polarization vector",is related with the electromagnetism phenomenon of the physics.
It means that the vector field that denotes the dipole moment of every single dielectric materials which is using in the electro magnetic field or using simply as the electricity conductor.
c)What is Self Inductance?
When there is a change in the current or magnetic flux of the coil, an electromotive force is induced. This phenomenon is termed Self Inductance. When the current starts flowing through the coil at any instant, it is found that, that the magnetic flux becomes directly proportional to the current passing through the circuit.
What is Mutual Inductance?
Consider two coils: P – coil (Primary coil) and S – coil (Secondary coil). A battery and a key are connected to the P-coil, whereas a galvanometer is connected across the S-coil. When there is a change in the current or magnetic flux linked with the two coils, an opposing electromotive force is produced across each coil, and this phenomenon is termed Mutual Inductance.