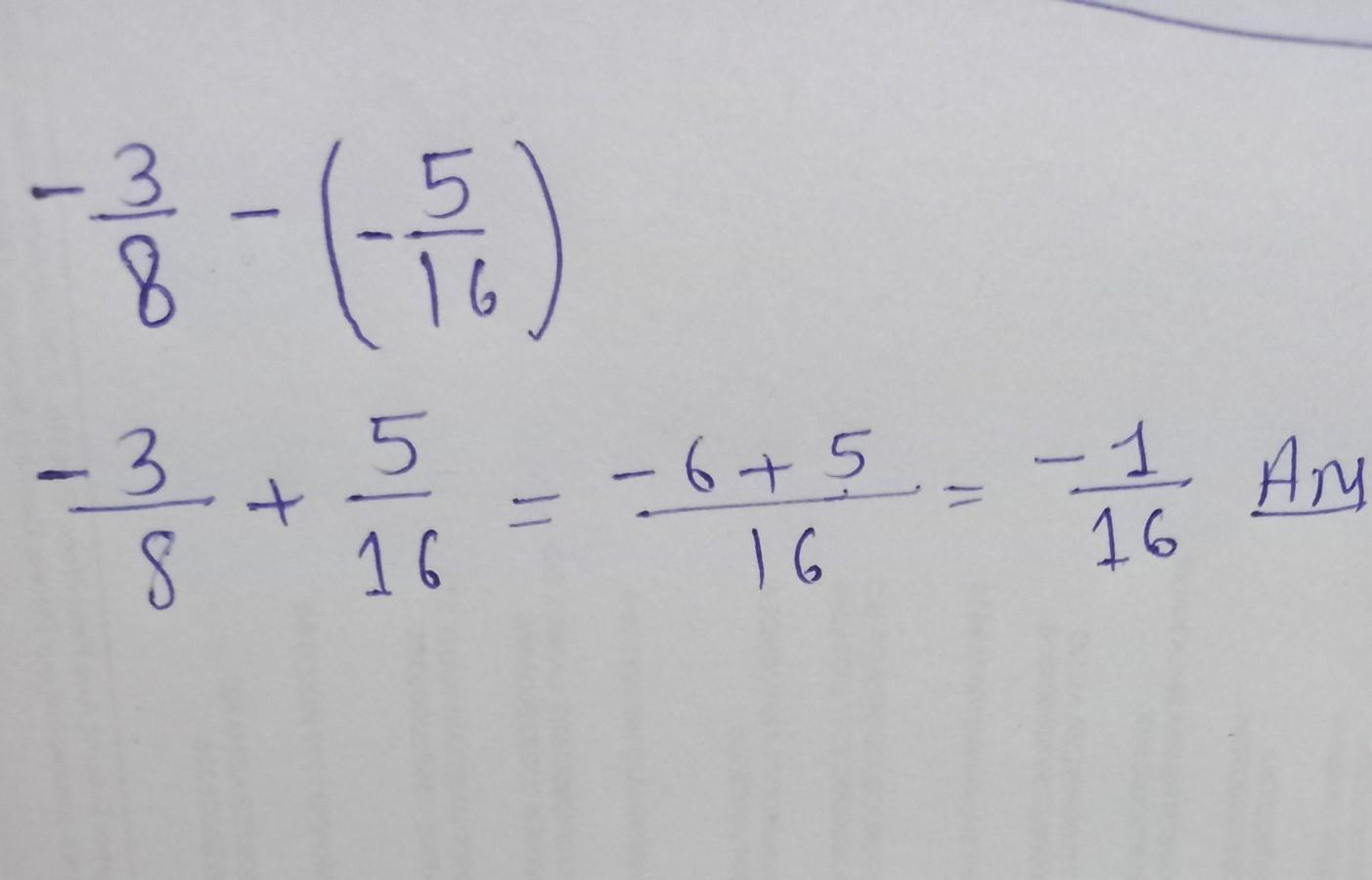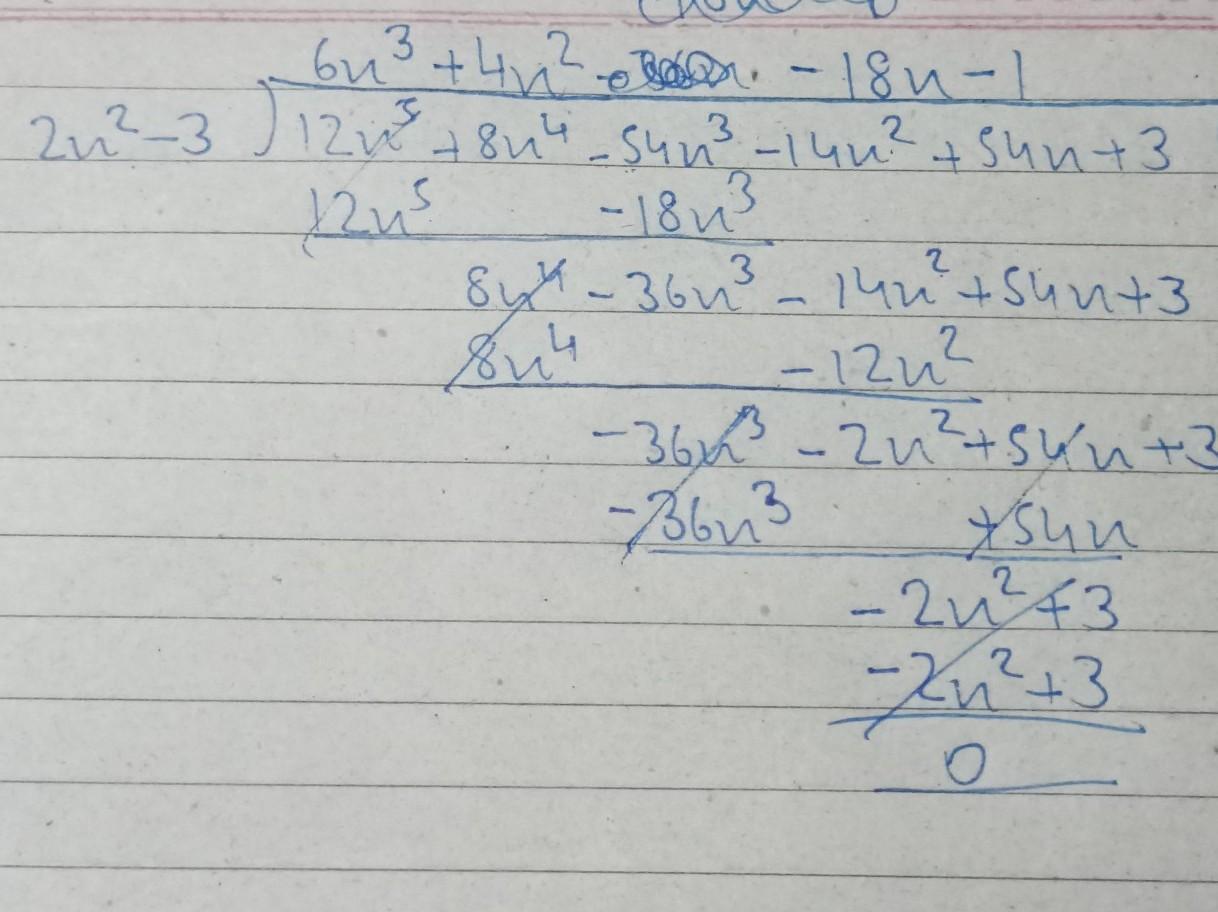a composition describing your idea of the perfect classroom
-
Subject:
History -
Author:
higginslogan -
Created:
1 year ago
Answers 1
What is 8 resistance combination ( b . a. d. )
hotiiiies
-
Author:
sonialam
-
Rate an answer:
10
If you know the answer add it here!
Choose a language and a region
How much to ban the user?
1 hour
1 day
100 years