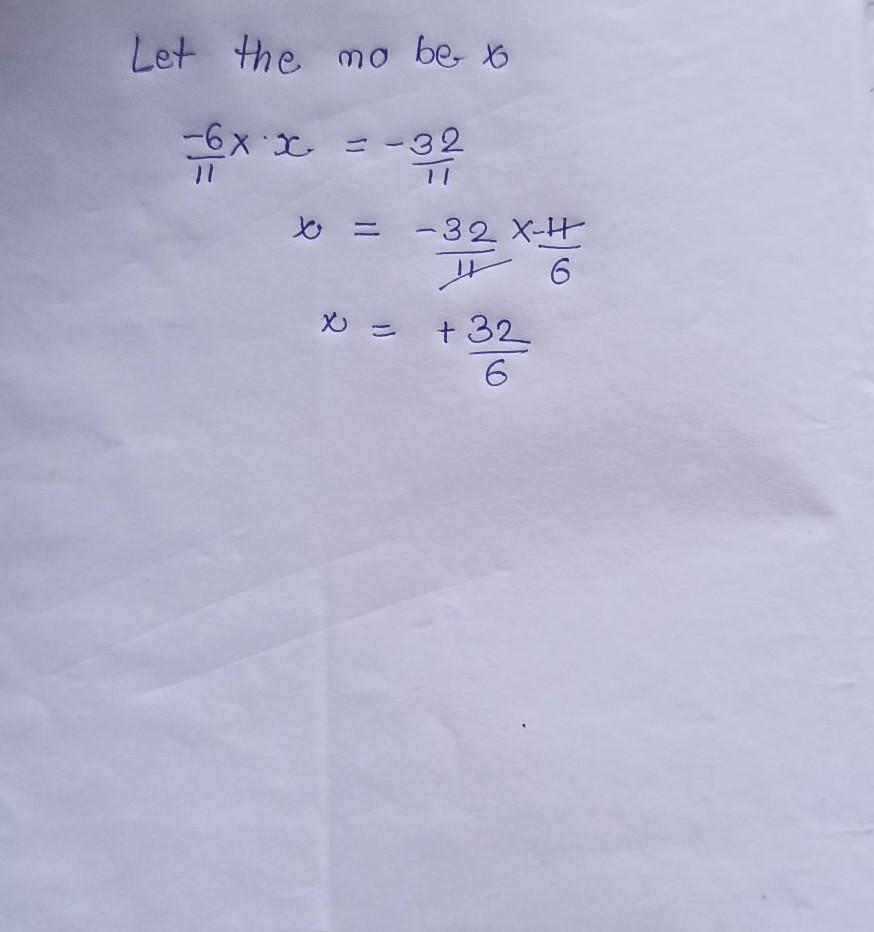Answer:
Concept:
A type of objective assessment known as a multiple choice, objective response, or MCQ asks respondents to choose just the right responses from a list of options. When a person must select amongst a variety of candidates, parties, or policies in an election or market research study, the multiple choice format is most usually utilized.
Given:
1. The amount of oil that flows each second is
a) 1x 10 m/s
b) 1x 10 m/s
c) 1x10 m/s
d) 1 m/s
2. The rate of oil flow in the pipe is
a) 10 x 10 m/s
b) 1.3 x 10 m/s
c) 20 x 10 m/s
d) 2.3 x 10 m/s
3. The difference in pressure between the pipe's ends is
a) 1.63 x 10- Pa
b) 2.63 x 10 Pa
c) 4 x 10- Pa
d) 6x 10 Pa
4. Reynolds's figure is
a) 0.00163
b) 0.0163
c) 0.163
d) 1.63
5. The pipe's oil flow is
a) laminar
b) turbulent
c) unstable
d) laminar as well as turbulent
Find:
Find the answers for the given questions
Answer:
1. (b) 1x 10 m/s
A student represent the volume of liquid that exits per second from a pipe of length l and radius r, where P represents the pressure differential between the pipe's two ends and represents the liquid's coefficient of viscosity, which has the dimensional formula [ML-1T-1].
2. (c) 20 x 10 m/s
The mathematical term for fluid motion is flow velocity, which is a vector field. The term "flow speed" refers to the entire length of the flow velocity. The vector field that gives fluids' velocities at specific times and locations is known as flow velocity.
3. (d) 6x 10 Pa
The pressure differential between a pipe's ends is halved and the radius is quadrupled while a liquid is flowing through it.
4. (d) 1.63
The Reynolds number is used to get some insight into the link between inertial forces, or those that continue moving due to Newton's first law that states that an item in motion doesn't stop, and viscous forces, or those that cause the fluid to cease flowing due to its viscosity.
It is a dimensionless number that controls how liquid flows through a conduit. It is described as the proportion of a fluid's inertial force to viscous force.
5. (d) laminar as well as turbulent
When a fluid flows in parallel layers with no interruption between the layers, it is known as laminar flow or streamline flow in pipes (or tubes). Adjacent layers tend to glide past one another like playing cards at low velocities since the fluid tends to move without lateral mixing.
Water flow is divided into numerous tiny flows with small cross sections by capillaries or tubes. There is less pressure and disturbance with a little flow. As the flow is divided into multiple flows, the turbulence of each flow decreases and each flow becomes laminar.
#SPJ3