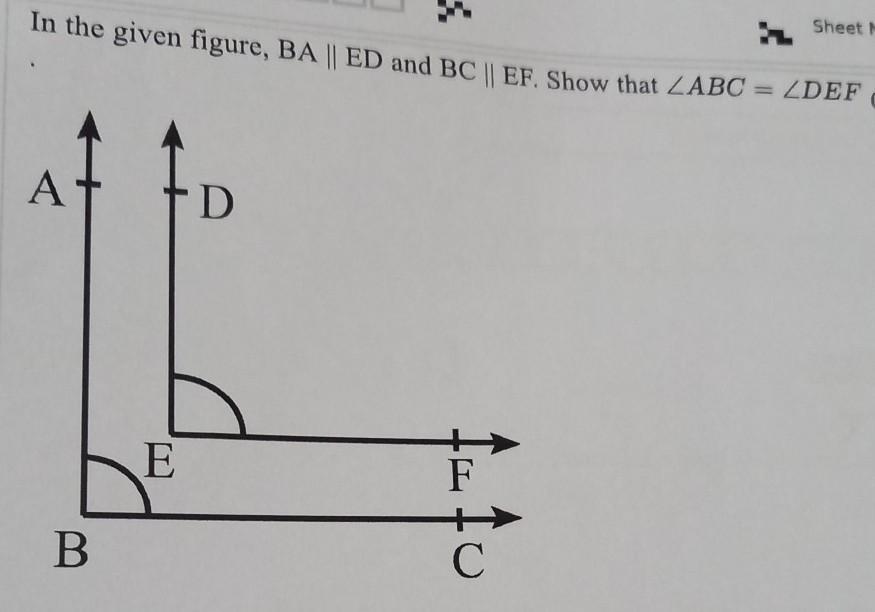
Let X = ABBDCB and Y=ABDCA. Find the LCS of X and Y. and its length. Show the details to answer the question.
-
Subject:
Computer Science -
Author:
jojo6cra -
Created:
1 year ago
Answers 1
Answer:
Explanation:Let us consider a sequence S = <s1, s2, s3, s4, …,sn>.
A sequence Z = <z1, z2, z3, z4, …,zm> over S is called a subsequence of S, if and only if it can be derived from S deletion of some elements.
Common Subsequence
Suppose, X and Y are two sequences over a finite set of elements. We can say that Z is a common subsequence of X and Y, if Z is a subsequence of both X and Y.
Longest Common Subsequence
If a set of sequences are given, the longest common subsequence problem is to find a common subsequence of all the sequences that is of maximal length.
The longest common subsequence problem is a classic computer science problem, the basis of data comparison programs such as the diff-utility, and has applications in bioinformatics. It is also widely used by revision control systems, such as SVN and Git, for reconciling multiple changes made to a revision-controlled collection of files.
Naïve Method
Let X be a sequence of length m and Y a sequence of length n. Check for every subsequence of X whether it is a subsequence of Y, and return the longest common subsequence found.
There are 2m subsequences of X. Testing sequences whether or not it is a subsequence of Y takes O(n) time. Thus, the naïve algorithm would take O(n2m) time.
Dynamic Programming
Let X = < x1, x2, x3,…, xm > and Y = < y1, y2, y3,…, yn > be the sequences. To compute the length of an element the following algorithm is used.
In this procedure, table C[m, n] is computed in row major order and another table B[m,n] is computed to construct optimal solution.
Algorithm: LCS-Length-Table-Formulation (X, Y)
m := length(X)
n := length(Y)
for i = 1 to m do
C[i, 0] := 0
for j = 1 to n do
C[0, j] := 0
for i = 1 to m do
for j = 1 to n do
if xi = yj
C[i, j] := C[i - 1, j - 1] + 1
B[i, j] := ‘D’
else
if C[i -1, j] ≥ C[i, j -1]
C[i, j] := C[i - 1, j] + 1
B[i, j] := ‘U’
else
C[i, j] := C[i, j - 1]
B[i, j] := ‘L’
return C and B
Algorithm: Print-LCS (B, X, i, j)
if i = 0 and j = 0
return
if B[i, j] = ‘D’
Print-LCS(B, X, i-1, j-1)
Print(xi)
else if B[i, j] = ‘U’
Print-LCS(B, X, i-1, j)
else
Print-LCS(B, X, i, j-1)
This algorithm will print the longest common subsequence of X and Y.
Analysis
To populate the table, the outer for loop iterates m times and the inner for loop iterates n times. Hence, the complexity of the algorithm is O(m, n), where m and n are the length of two strings.
Example
In this example, we have two strings X = BACDB and Y = BDCB to find the longest common subsequence.
Following the algorithm LCS-Length-Table-Formulation (as stated above), we have calculated table C (shown on the left hand side) and table B (shown on the right hand side).
In table B, instead of ‘D’, ‘L’ and ‘U’, we are using the diagonal arrow, left arrow and up arrow, respectively. After generating table B, the LCS is determined by function LCS-Print. The result is BCB.
LCS
-
Author:
kieran
-
Rate an answer:
12