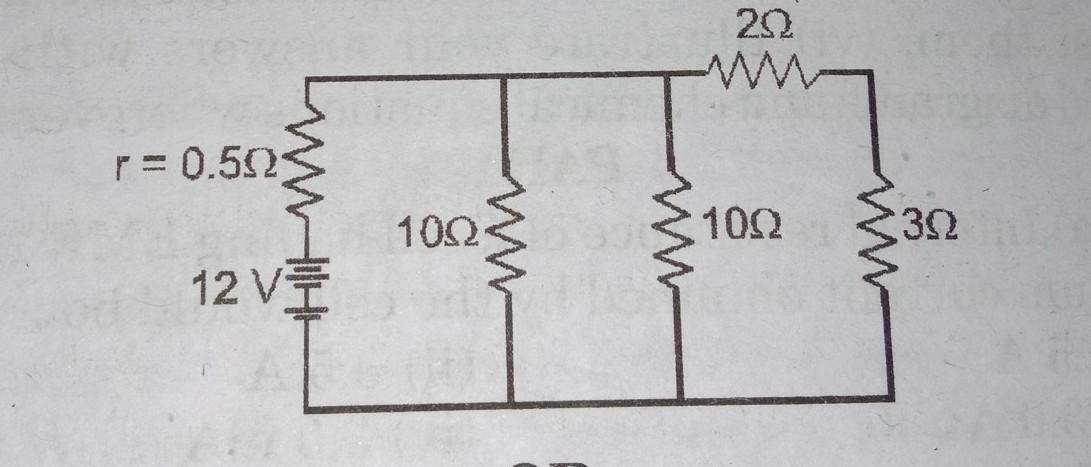
explain any four important of minutes
-
Subject:
Business Studies -
Author:
rigoberto98 -
Created:
1 year ago
Answers 2
Minutes record meeting decisions, which makes them a useful review document when it comes time to measure progress. They also act as an accountability tool because they make it clear who's duty it was to perform which action.
-
Author:
lokilaeu
-
Rate an answer:
5
Minutes serve to both memorialize the actions taken for those attending the meeting as well as for those who were unable to attend the meeting.
-
Author:
nibbysolomon
-
Rate an answer:
4
If you know the answer add it here!
Choose a language and a region
How much to ban the user?
1 hour
1 day
100 years